Automated PDF redaction/de-identification: Performance Analysis
Today, keeping sensitive information safe is more important than ever. Organizations frequently han…
gerger
Medical images stored in DICOM format contain a wealth of sensitive information, including patient names, dates of birth, medical record numbers, and anatomical details. Unauthorized access to this information can lead to breaches of patient privacy, identity theft, and legal repercussions for healthcare providers. DICOM de-identification mitigates these risks by stripping identifiable data from images, ensuring that only authorized individuals have access to patient information.
Healthcare organizations must adhere to stringent regulations such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the United States and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe, which mandate the protection of patient data. DICOM de-identification is essential for compliance with these regulations, as it helps healthcare providers meet their legal obligations while facilitating data sharing for research and clinical purposes.
DICOM de-identification promotes data sharing and collaboration among healthcare professionals, researchers, and institutions. By anonymizing patient information, DICOM images can be shared more freely for educational purposes, multi-center studies, and quality improvement initiatives, leading to improved patient outcomes and advancements in medical science.
DICOM document can contains PHI and PII in four places:
DICOM metadata contains in most cases contains PHI. Below are some common examples of Protected Health Information (PHI) often present in DICOM metadata:
"Burned-in pixel data" refers to image information permanently embedded within the image itself, becoming an inseparable component of the pixel data. This integration makes the information resistant to easy removal or modification since it's part of the image's raw data.
This is most challanged and expensive part because pixel data is big. Some time size of one frame can be 1..2 GB, and our solution support process DICOM files up to 4 GB.
Another challenage with pixel data is various color schema and compression. ApicomPro's solution support following color schemas(PhotometricInterpretations) in DICOM:
"Overlay data" denotes additional graphical or textual elements that can overlay medical images, serving to provide annotations, measurements, or other enhancing information for interpretation. This overlay data is structured into overlay planes, each representing a distinct layer of graphical or textual data superimposable on the primary image. Multiple overlay planes enable the addition of various types of annotations or information to an image.
Encapsulated Documents in DICOM are utilized to associate textual or document-based information with medical images. These documents may encompass clinical reports, patient histories, annotations, or any other relevant textual data. DICOM Encapsulated Documents support various formats such as PDF, HTML, or plain text, with the format typically specified within the DICOM object.
For single frame documents we able to run REST API service and scale it horisontaly by contanerisation.
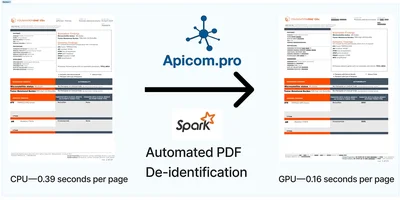
For multiframe documents prefer to run pipeline on the Spark and distribute processing each frame. This approach give capability handle really big files, we have expiriance with 3..4 GB files and southands of frames.

Today, keeping sensitive information safe is more important than ever. Organizations frequently han…

In the healthcare industry, the handling of medical documents is governed by stringent regulations …
Discover how ApicomPro can help you de-identify Dicom and comply with data protection regulations. Contact us today to learn more about our solutions and request a demo.